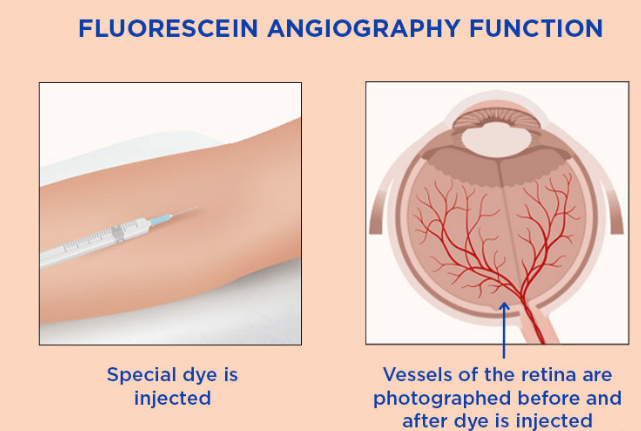
Retinal angiography is a minimally invasive eye imaging test that evaluates retinal and choroidal blood circulation. Using special dyes and advanced imaging, it plays a crucial role in diagnosing retinal, choroidal, and optic nerve diseases. It is an essential part of multimodal imaging in ophthalmology.
The results of retinal angiography help ophthalmologists, make accurate diagnoses and guide treatment decisions for various eye conditions.
✔ Outpatient procedure with dilated pupils
✔ Intravenous injection of dyes (fluorescein, indocyanine green, or both)
✔ Sequential fundus photography over 5 to 20 minutes
✔ Rare side effects, typically mildnYour ophthalmologist will provide a detailed explanation of the procedure and answer any questions you may have.
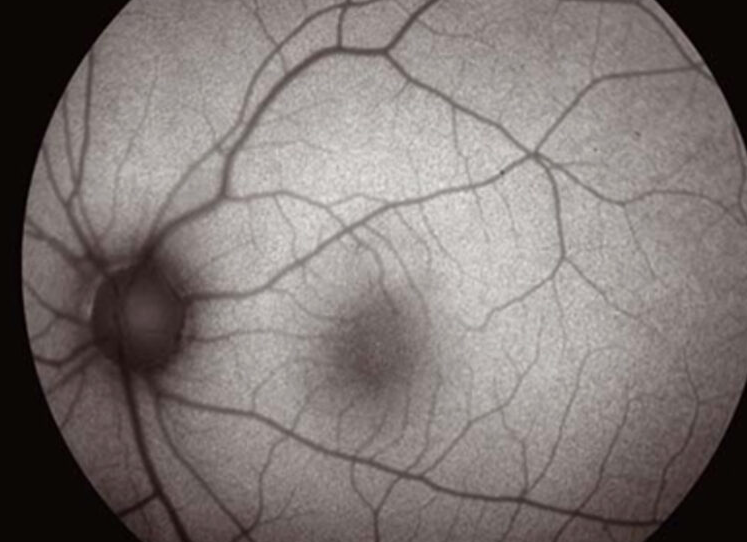
Retinal autofluorescence (FAF) is a non-invasive imaging technique that detects dysfunctions in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). This layer is essential for maintaining a healthy retina.Autofluorescence helps map lipofuscin accumulation—a key indicator of retinal aging and disease—as well as other abnormal fluorophores that may build up in retinal and subretinal spaces.
FAF is useful in diagnosing and monitoring:
🔹 Retinopathies (diabetic retinopathy, hereditary retinal diseases)
🔹 Choroidopathies
🔹 Pseudo-edema of the optic nerve head
🔹 Retinal and choroidal tumors
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a quick, non-invasive imaging test that provides high-resolution cross-sectional (2D and 3D) images of the eye’s structures.OCT works through laser interferometry, using infrared light to analyze reflected and absorbed signals from different layers of the eye. Unlike traditional CT scans, OCT does not use radiation, making it a safe and highly precise diagnostic tool.OCT has become an essential imaging method for diagnosing and monitoring many eye conditions.
OCT is crucial for detecting and managing:🟢 Macular diseases (central retina):
✅ Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
✅ Diabetic maculopathy
✅ Retinal vein occlusions
✅ Posterior uveitis, CSR, post-surgical maculopathies
✅ Vitreomacular interface disorders🟢 Peripheral retinal and choroidal conditions:
✅ Retinal and choroidal tumors
✅ Retinal detachment, retinoschisis🟢 Optic nerve disorders:
✅ Glaucoma (all types)
✅ Ischemic, compressive, toxic, and infiltrative optic neuropathies
✅ Optic nerve swelling (papilledema, pseudo-papilledema)🟢 Corneal diseases:
✅ Keratoconus
✅ Corneal scarring, corneal thinning, corneal abscesses🟢 Iridocorneal angle disorders:
✅ Angle-closure glaucoma
✅ Tumors of the iridocorneal angle
If you have vision changes, retinal disease, or need advanced eye imaging, Centre ophtalmologique du Glacis offers state-of-the-art angiography, autofluorescence, and OCT imaging